学术快讯 | 建筑室外空间微气候的逆向设计:以高密度环境下的幼儿园室外空间为例
近日,上海交通大学设计学院建筑学系建筑技术团队研究生孙睿以第一作者身份,在高水平国际期刊《Energy and Buildings》(影响因子IF=7.201,JCR Q1)上发表了学术论文“Building Form and Outdoor Thermal Comfort: Inverse Design the Microclimate of Outdoor Space for a Kindergarten”。该论文提出了基于计算流体力学和遗传算法的室外热舒适逆向设计方法,并将该方法应用于上海和天津气候条件下的幼儿园室外空间设计。

1 论文摘要
舒适的室外微气候对于创造吸引市民、增强城市活力的优质户外空间至关重要。以往改善室外热舒适的设计研究通常在大尺度进行,如城市尺度、街区尺度等。然而,很少有研究关注建筑尺度。本研究提出了一种基于遗传算法的逆向优化流程,以在早期设计阶段确定建筑的形状、朝向和位置,从而降低目标场地的室外时均冷热应力。在优化流程中,本研究对太阳辐射场和风场进行模拟,并以UTCI作为室外热舒适评价指标,模拟的准确性由实验数据加以验证。随后,本研究将该优化框架应用于天津和上海气候条件下的幼儿园室外空间设计。结果表明,优化可以降低目标场地的室外时均冷热应力,并给出热应力最低的幼儿园形态布局。此外,在优化过程中,本研究还发现太阳辐射场对室外热舒适的影响大于风场,且缓解热应力比缓解冷应力对提升室外空间品质更为有效。本研究提出了基于建筑尺度的室外热舒适逆向设计方法,并为创建舒适的城市室外空间提供了设计建议。
关键词:遗传算法,辐射,风,CFD,UTCI,热应力
1 Abstract
Thermally comfortable mircoclimate is essential for creating high-quality outdoor spaces that attract citizens and boost city vitality. Previous design efforts to improve outdoor thermal comfort were usually conducted at large scales, such as city scale, neighborhood scale, urban block scale. Few researchers focused on the building scale. This study proposes an optimization framework based on genetic algorithm to determine the building shape, orientation, and location during early design stage that reduces the overall thermal stress in the target outdoor space. Solar radiation and wind fields were simulated to obtain the outdoor Universal Thermal Climate Index (UTCI) as the performance indicator. The simulations were validated against the experimental data. This investigation applied the proposed optimization framework to design the outdoor space for a kindergarten under the climate of Tianjin and Shanghai, respectively. The results showed that optimization reduced the overall thermal stress. The most favourable kindergarten forms were suggested through optimization. Moreover, solar radiation has been proved to contribute more to outdoor thermal comfort than wind field and heat stress is more important than cold stress during optimization. This study supplements the inverse design of outdoor thermal comfort at building scale and provides suggestions to create comfortable urban outdoor spaces.
Keywords: Genetic algorithm;Radiation;Wind;CFD;UTCI;Thermal stress
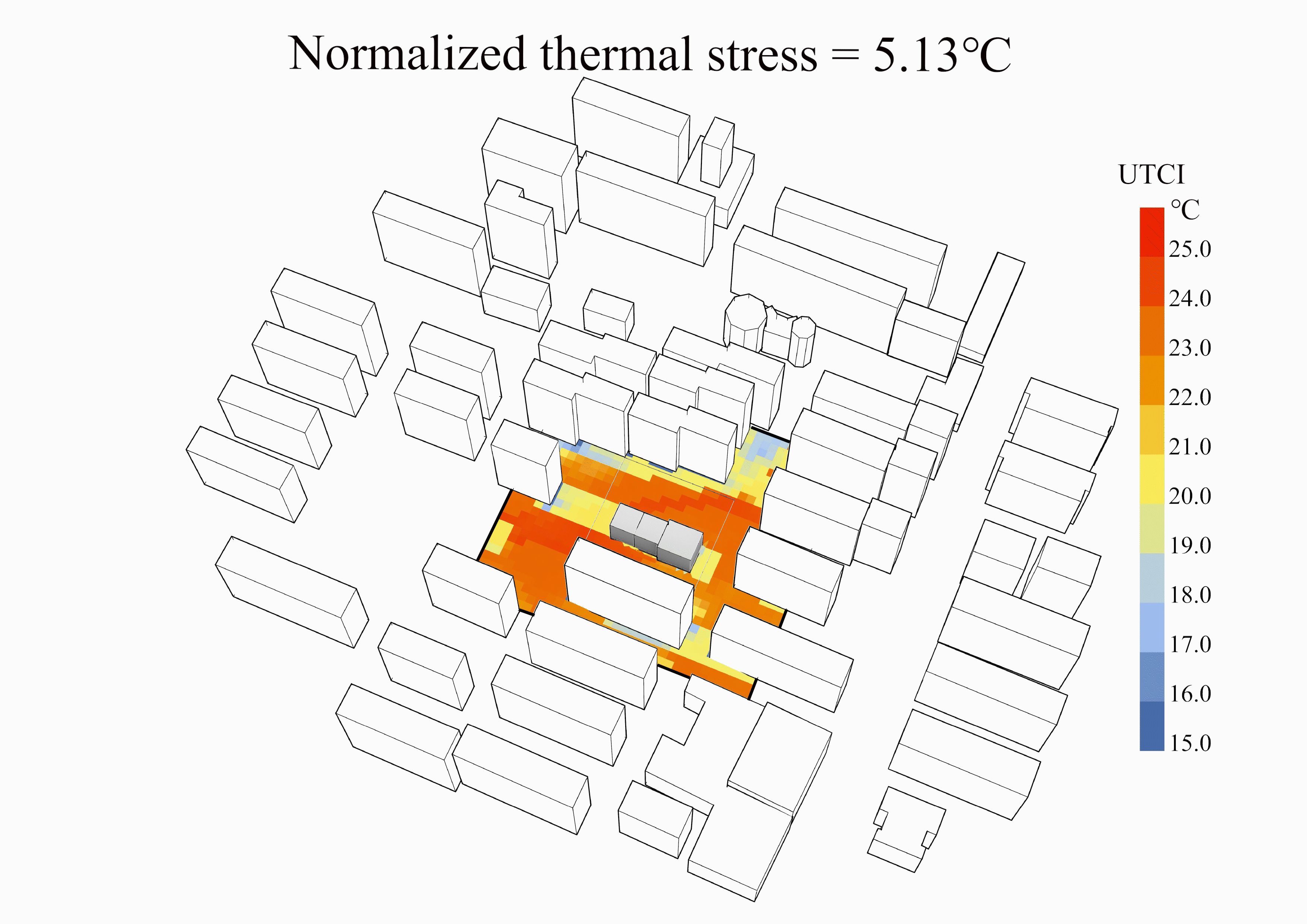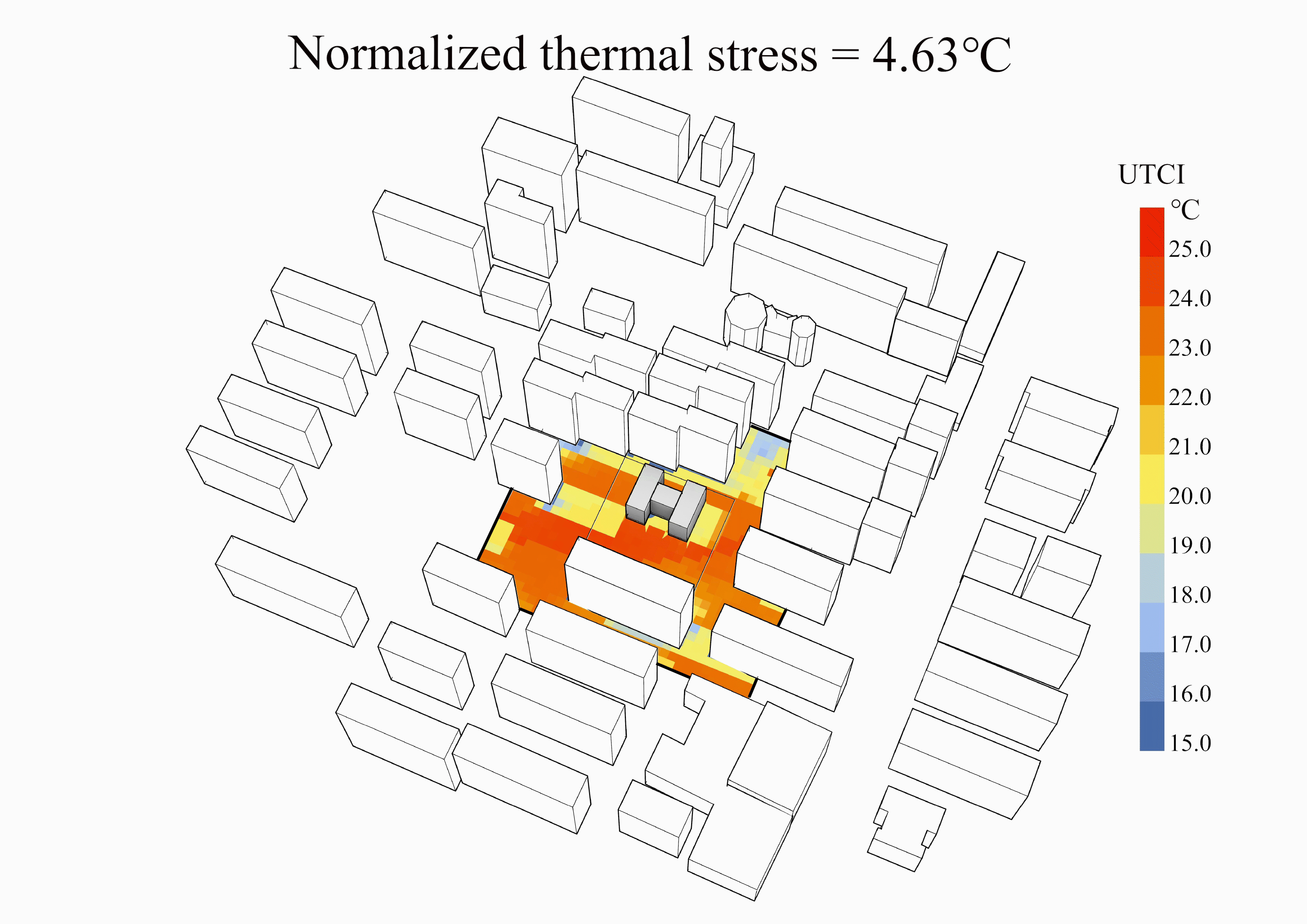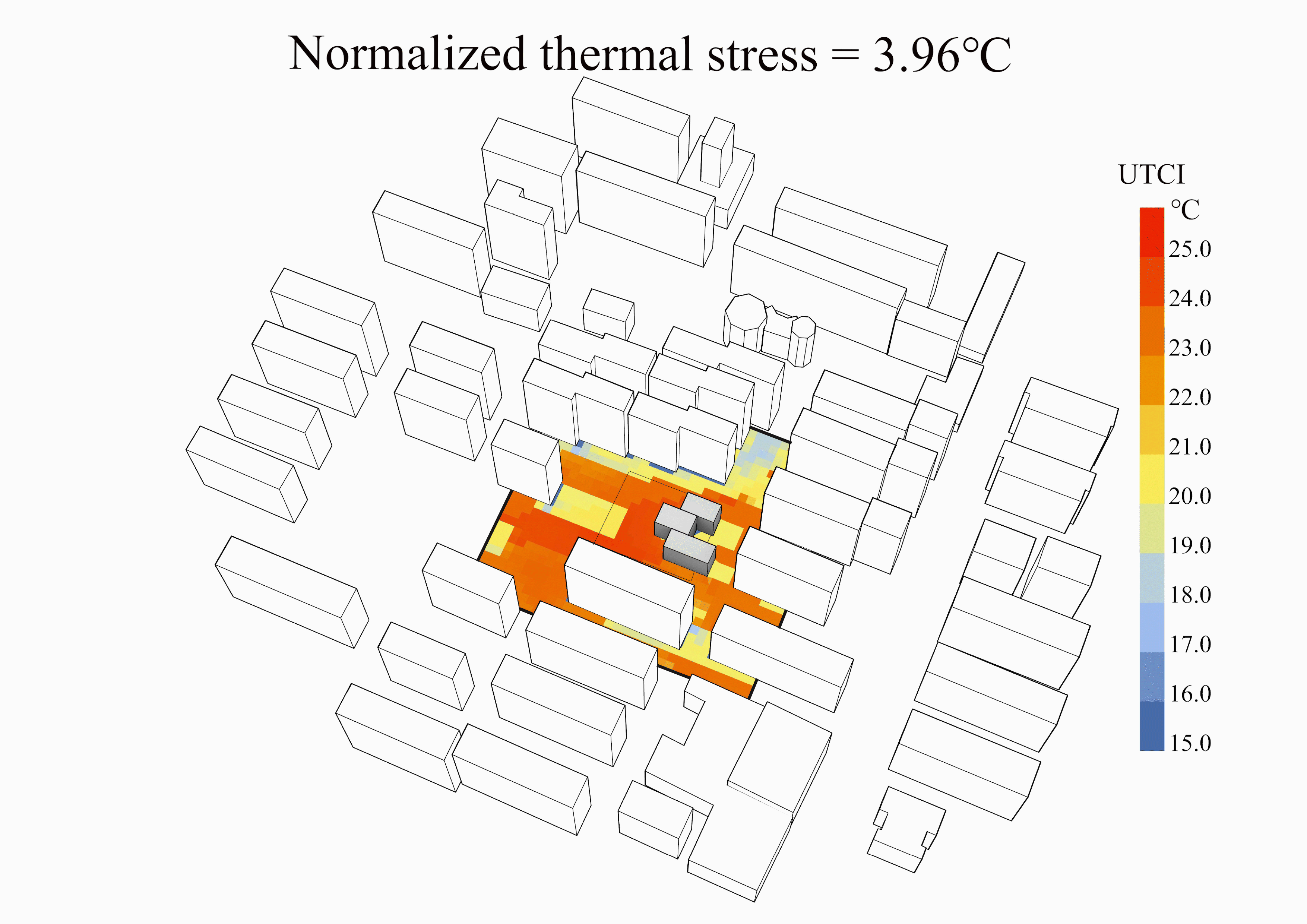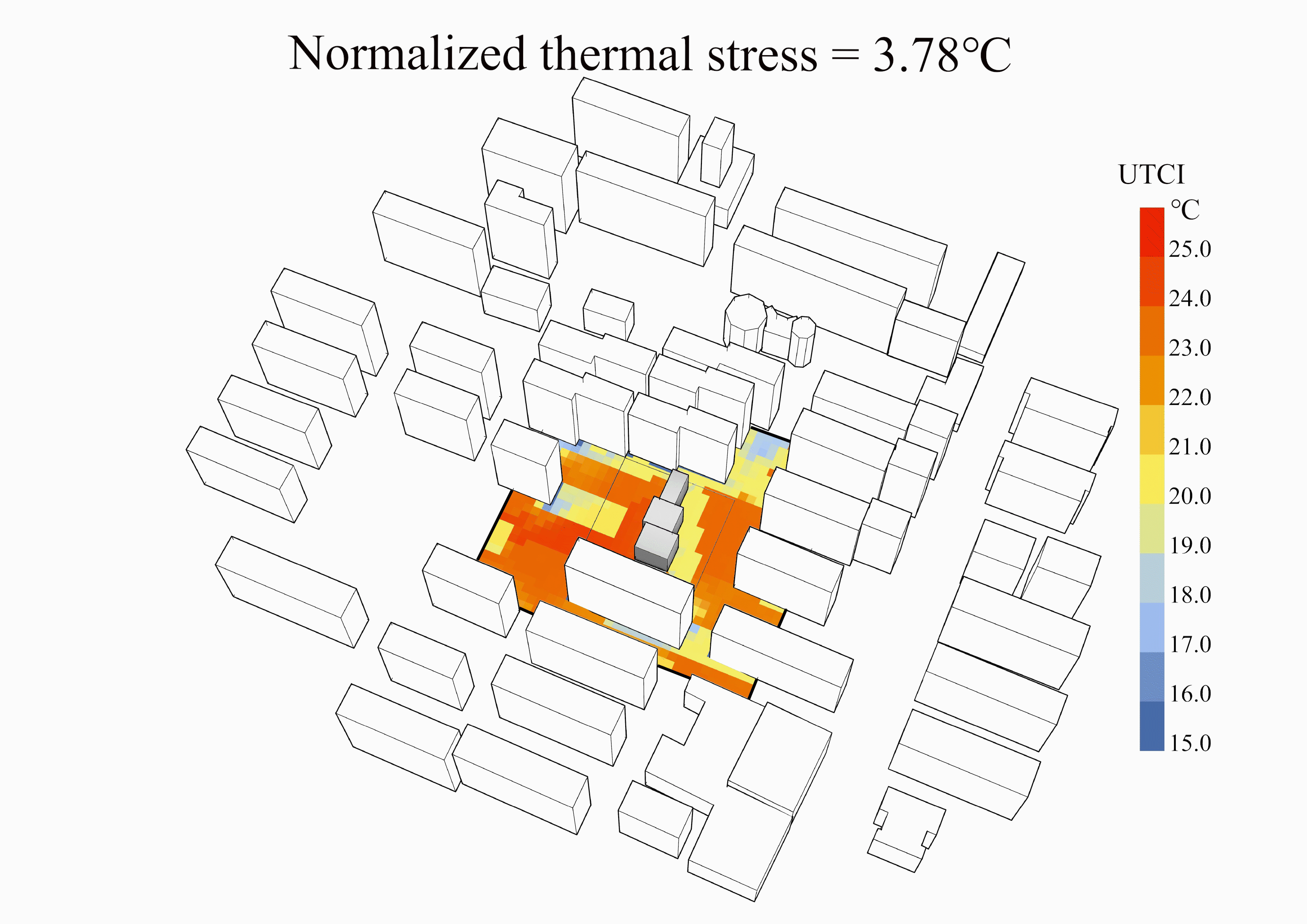
某高密度住区中幼儿园室外空间热环境逆向设计
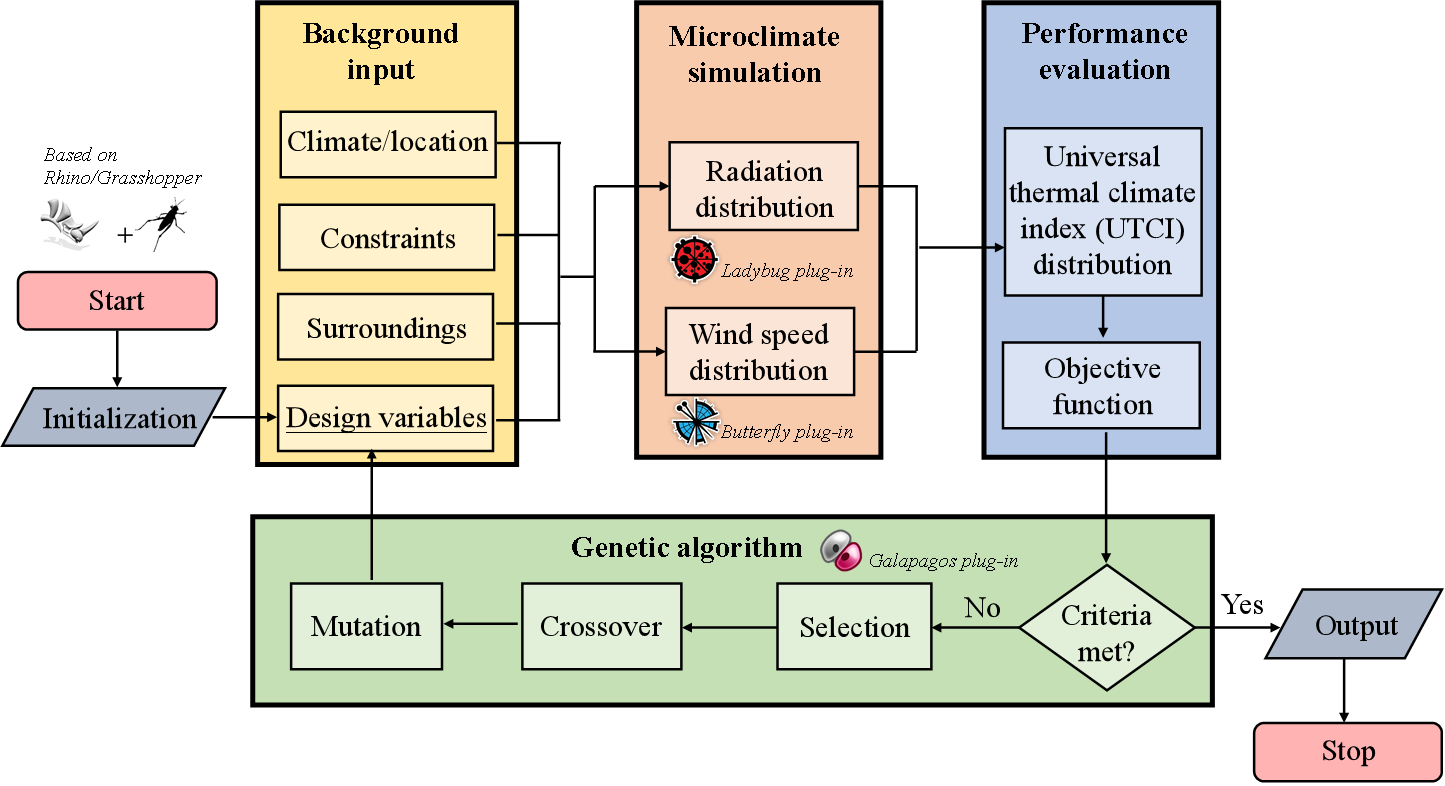
研究流程

参数化生成建筑形体与位置

目标函数随优化代数的变化:上海案例

上海案例中计算场地、最差设计、冬季最优设计、夏季最优设计和最优设计的风场、平均辐射温度场和UTCI场云图
该论文共同通讯作者为上海交通大学设计学院建筑学系建筑技术团队赖达祎副教授和瑞典皇家理工学院土木与建筑工程系刘炜副教授,合作作者为天津大学天津市室内空气质量控制重点实验室刘俊杰教授。建筑学系本科生吴媛媛,左亚汐,陈迪,徐羽伦参与了“基于风光定位的室外空间自动逆向寻优设计研究”PRP项目,对本文亦有贡献。